コレクション dural venous sinuses anatomy ppt 148261-Dural venous sinuses anatomy ppt
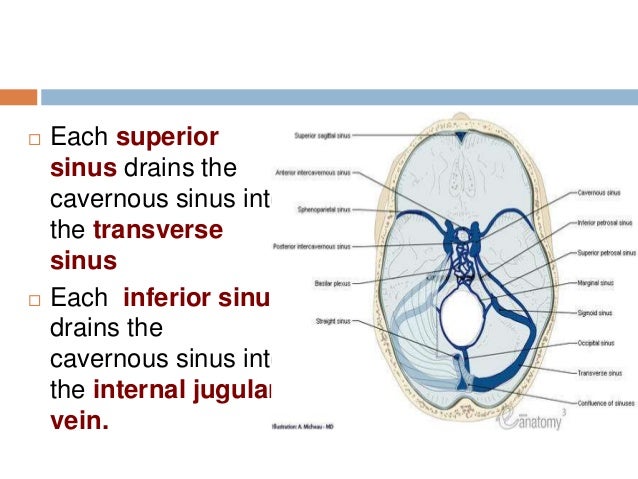
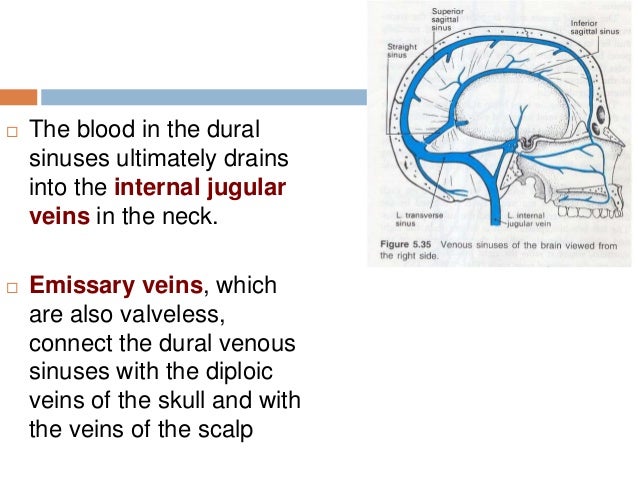
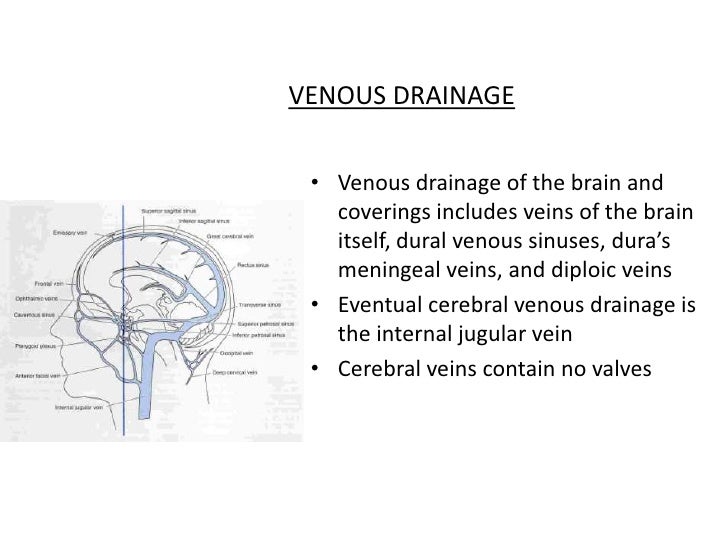
· VENOUS DRAINAGE • Venous drainage of the brain and coverings includes veins of the brain itself, dural venous sinuses, dura's meningeal veins, and diploic veins • Eventual cerebral venous drainage is the internal jugular vein • Cerebral veins contain no valves 15 Vasculature Venous Sinuses 16Find PowerPoint Presentations and Slides using the power of XPowerPointcom, find free presentations research about Dural Venous Sinuses PPT About 14 results (139 seconds) Sponsored Links Displaying dural venous sinuses PowerPoint Presentations Neurosyphilis Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Gummas, Aortitis, Chorioretinitis Three Major Syndromes Tabes PPTCranial meninges, dural venous sinuses (cavernous sinus) and cerebrospinal fluid are shown in this dissection using a human cadaver Orig air date MAY 16 7
Gmegjdddoez0zm
Dural venous sinuses anatomy ppt
Dural venous sinuses anatomy ppt-Dural venous sinuses are venous channels located intracranially between the two layers of the dura mater (endosteal layer and meningeal layer) They can be conceptualised as trapped epidural veins Unlike other veins in the body, they run alone, not parallel to arteries Furthermore, they are valveless, allowing for bidirectional blood flow in intracranial veins It is also important to noteFunctional anatomy • The dural sinuses are designed to maintain the patency in the face of negative pressure • Their triangular shape make them relatively non compressible • Bridging vein entering the sinuses opposite the direction of sinus blood flow • There are no valves • Their wall contain noradrenergic & peptidergic fibres Cerebral venous system physiology Role in




The Head Skull And Meninges Ppt 1 Flashcards Quizlet
15(6) 499–519 Crossref, Medline, Google ScholarOther dural venous sinuses This explains the frequent occurrence of CVT as a complication of infective pathologies in the catchments areas eg cavernous sinus thrombosis in facial infections, lateral sinus thrombosis in chronic otitis media and sagittal sinus thrombosis in scalp infections16 The dural sinuses especially the SSS contain most of the arachnoid villi and granulations, in · Purpose Magnetic resonance venography (MRV) has not been validated in preoperative planning of the dural venous sinus stenting (VSS) among idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) patients We aim to prospectively evaluate dural venous sinus measurement in IIH patient population on twodimensional timeofflight (2DTOF) MRV and Threedimensional
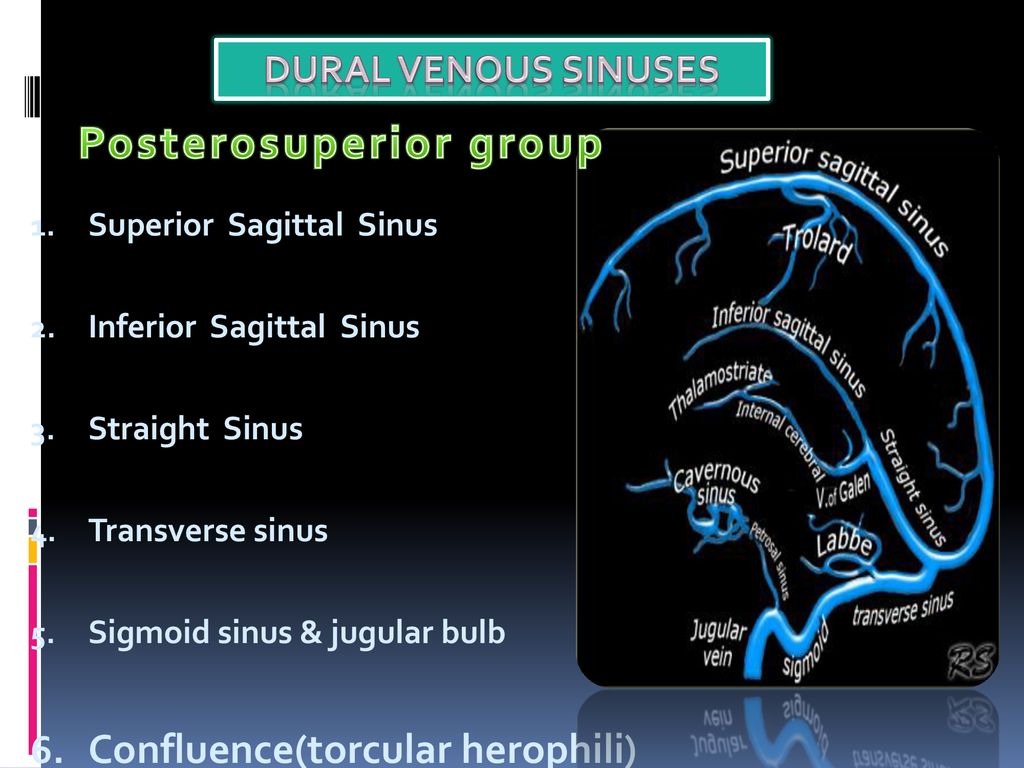
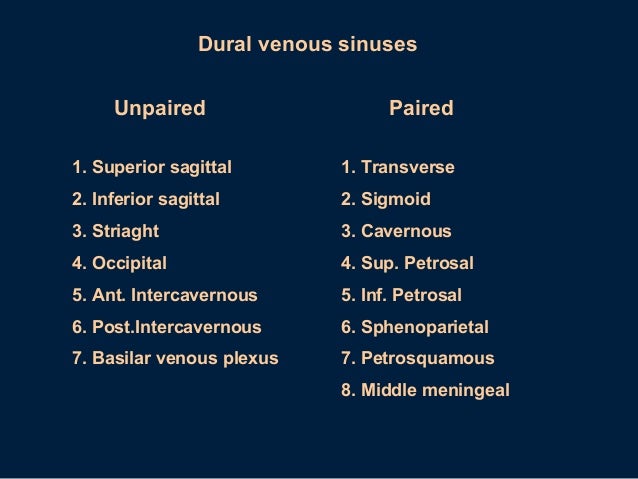
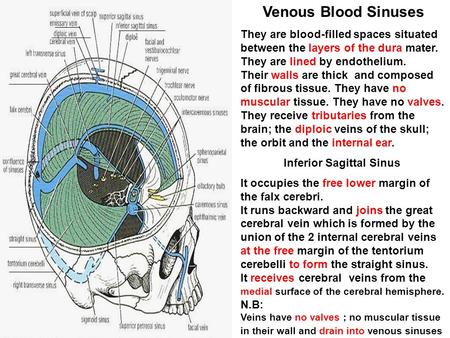
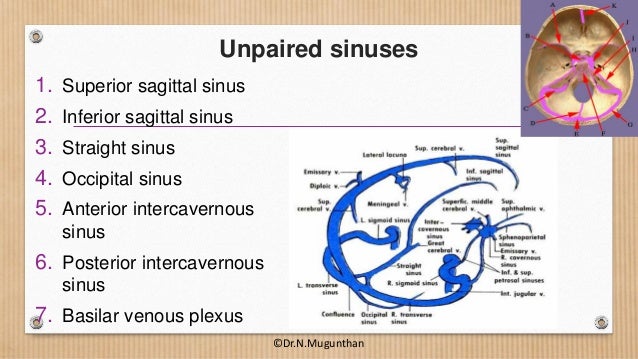
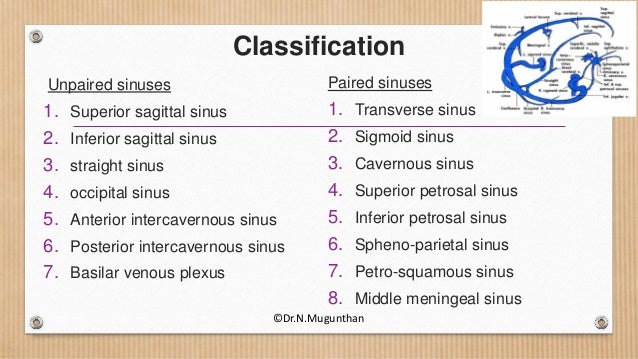
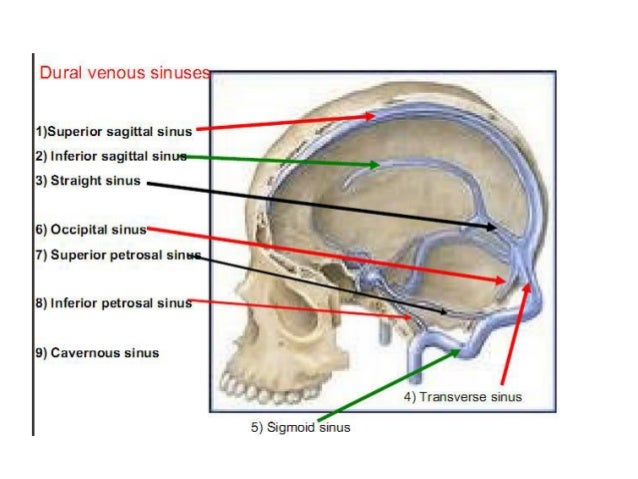
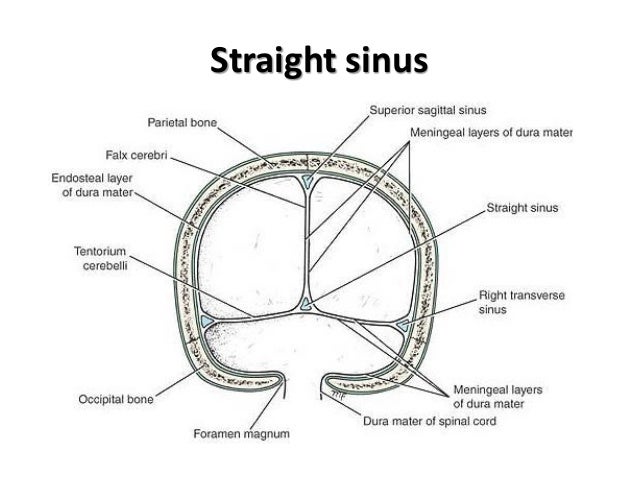
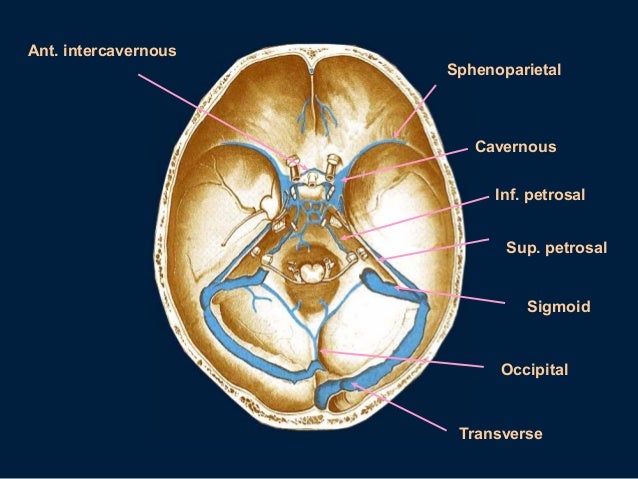
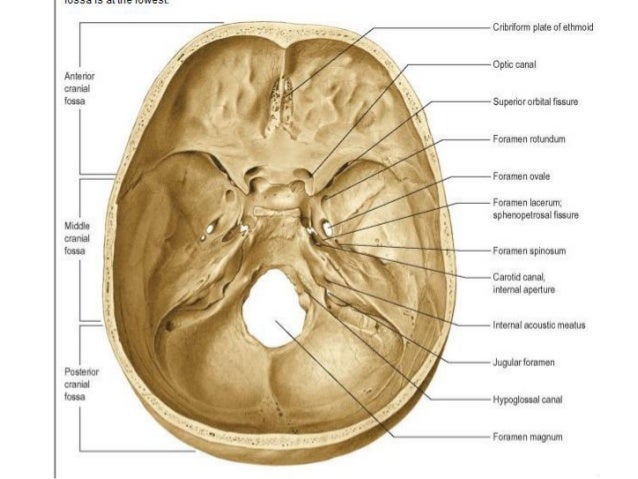
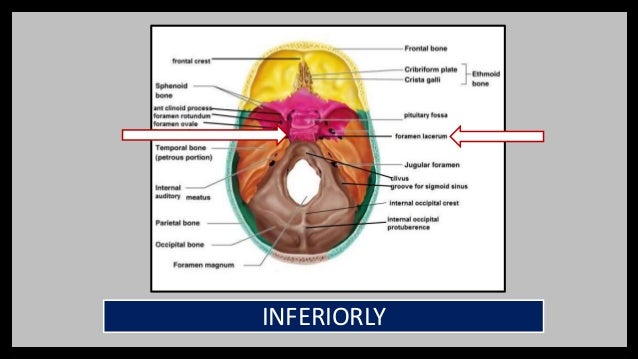
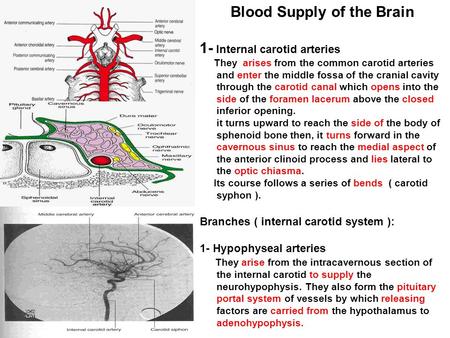
Purchase Anatomy, Imaging and Surgery of the Intracranial Dural Venous Sinuses 1st Edition Print Book & EBook ISBN , · Dural venous sinuses The human brain has the highest demand for oxygen of any tissue in the human body It receives a vast amount of blood from two systems the internal carotid system anteriorly, and the vertebrobasilar system posteriorly However, there is very little space in the cranial vault to accommodate large amounts of bloodDural venous sinuses There are seven paired (transverse, cavernous, greater & lesser petrosal, sphenoparietal, sigmoid and basilar) and five unpaired (superior & inferior sagittal, straight, occipital and intercavernous) dural sinuses There are two sagittal sinuses that occupy the longitudinal cerebral fissure (midline between the cerebral
Anatomy and Function of the Dural Venous Sinuses Dural venous sinuses are venous blood reservoirs contained between the two layers of the dura mater Absence of lymphatic drainage in the brain places the venous outflow system at a pedestal of prime importance Following a prologue to dural venous sinuses, this article focuses on arachnoid granulations, tributaries and theLearn and reinforce your understanding of Anatomy of the cranial meninges and dural venous sinuses through video Anatomy of the cranial meninges and dural venous sinuses Osmosis is an efficient, enjoyable, and social way to learn Sign up for an account today!If you like the video than like it, Subscribe it and share with your friends Do not forget to click on Bell icon and never miss the new video If you do not



Dural Venous Sinuses 4 27 17 Lufukuja G Ppt Video Online Download



Dural Venous Sinuses Cavernous Sinus Dr N Mugunthan
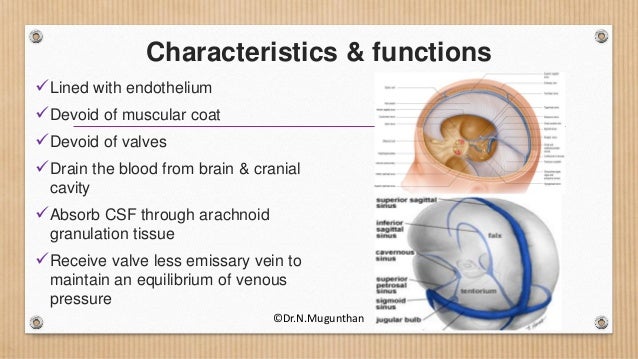
DURAL VENOUS SINUSES definition 1Venous spaces present between the two layers of dura 2Lined by endothelium 3Devoid of valves definition 4Do not have muscle coat in their tunica adventitia 5Contain CSF Classification Paired and unpaired Paired are Cavernous sinuses J Petrosal sinuses H,I Transverse sinuses G Sigmoid sinuses C Sphenoparietal sinuses A2902 · Anatomy ☠️ ð § MedNotes ð § Anatomy is the subject every medical student is scared of We bring you Anatomy Notes to help you out Anatomy Notes include all the important topics you need to learn and do better in the exam From General Anatomy to regional anatomy, Anatomy Notes include it all These notes are handwritten by and for62(8) 1445–1446 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar;



Ppt Chapter 21 The Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels And Hemodynamics Powerpoint Presentation Id



15 Dural Venous Sinuses
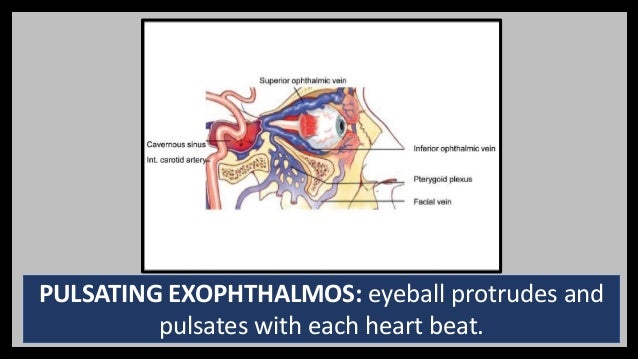
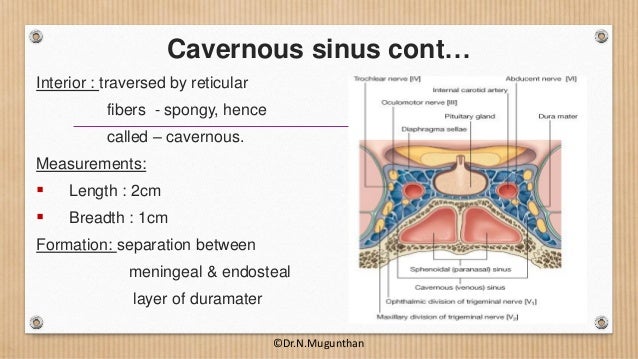
Anatomy Cavernous sinus Dura mater Microsurgery abstract The external structure of each cavernous sinus (CS) is made of four dural walls The aim of this study was to describe the anatomy of the dural walls of the CS We studied 42 adult cadaveric heads, fixed with formalin and injected with coloured silicon The main findings were (i) the · The cavernous sinus is a paired dural venous sinus located within the cranial cavity It is divided by septa into small 'caves' – from which it gets its name Each cavernous sinus has a close anatomical relationship with several key structures in the head, and is arguably the most clinically important venous sinus In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the cavernous sinusObstruction of the intracranial dural venous sinuses would result in an increase in intracranial dural venous pressure This intracranial hypertension is not only the result of poor cerebral venous drainage but also life threatening The aim of this study was to identify the structures, which may show signs of potential venographic filling defect qualities, including trabeculae/septa (also



15 Dural Venous Sinuses




Ppt Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Cvst Causes Risks Complications Diagnosis And Treatment Powerpoint Presentation Free To Download Id 871a23 Njjhn
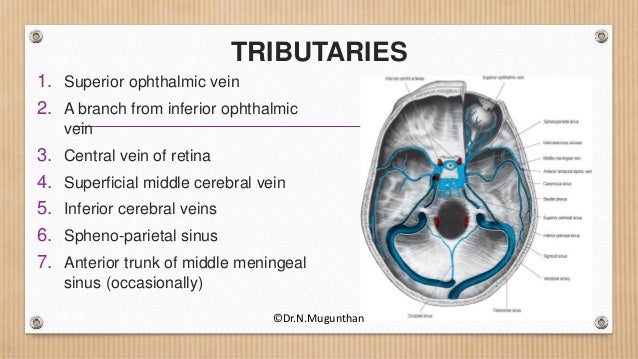
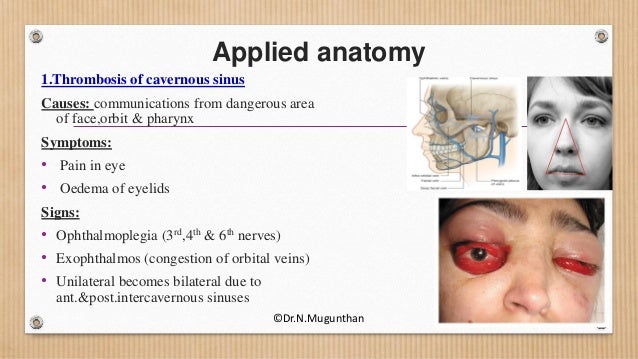
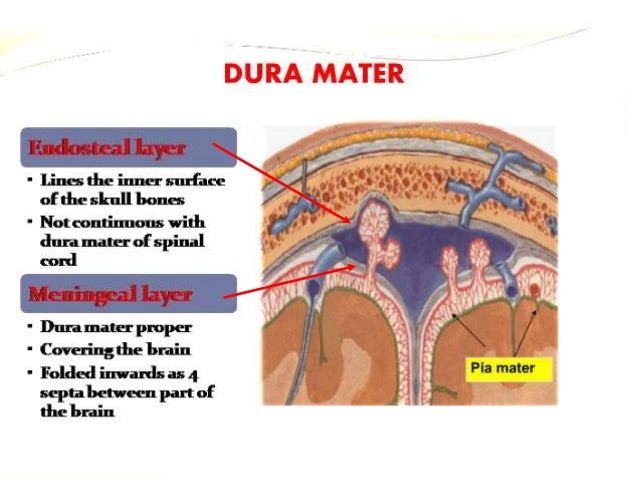
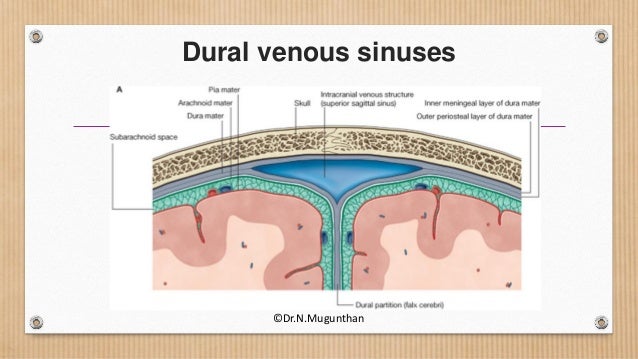
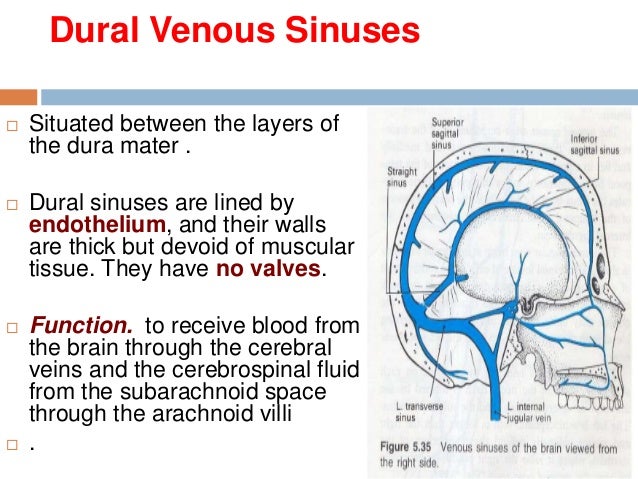
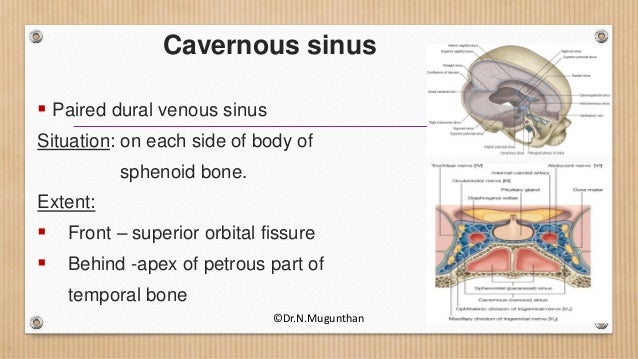
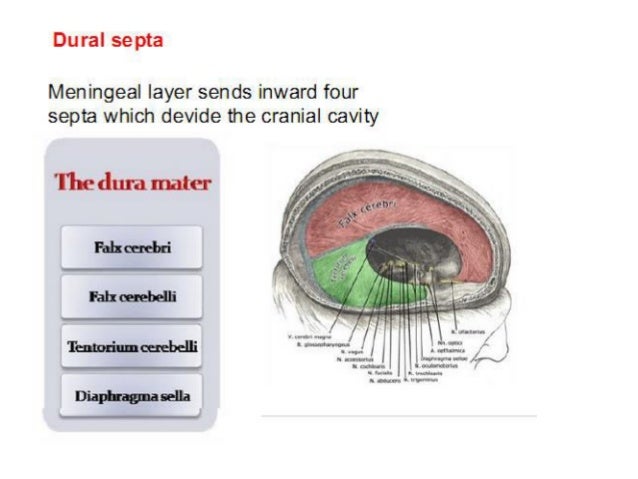
This page was last edited on 16 May 21, · 15 dural venous sinuses 1 DURAL VENOUS SINUSES Dr Hafsa Nisar 3 CEREBRAL DURA MATER ENDOSTEAL LAYER MENINGEAL LAYER 4 TENTORIUM CEREBELLI 5 Dural Venous Sinuses Situated between the layers of the dura mater Dural sinuses are lined by endothelium, and their walls are thick but devoid of muscular tissue · Sphenoparietal sinus 7 Petrosquamous sinus 8 Middle meningeal sinus ©DrNMugunthan 8 Cavernous sinus Paired dural venous sinus Situation on each side of body of sphenoid bone Extent Front – superior orbital fissure Behind apex of petrous part of temporal bone ©DrNMugunthan 9



Cerebral Venous Anatomy And Ppt Download



Venous Dural Sinuses And Cavenous Venous Sinus
Anatomy and Physiology of the Nose and Paranasal Sinuses PD Dr med Basile N Landis Unité de RhinologieOlfactologie Service d'OtoRhinoLaryngologie et de Chirurgie cervicofaciale, Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève, Suisse · Intracranial dural AV fistulas (dAVF, aka dural AV fistulas, dural arteriovenous fistulous malformation (Borden et al, J Neurosurg 166–179, 1995)) are acquired lesions that usually involve one of the intracranial venous sinuses They comprise ≤10% of all intracranial vascular malformations (AlShahi et al, Stroke –1169, 03) Typically, numerous · The occipital sinus, which is the smallest dural venous sinus, runs along the inner surface of the occipital bone The occipital sinus is attached to the posterior margin of the falx cerebelli and receives tributaries from the margins of the foramen magnum It may anastomosis with the sigmoid sinuses and posterior internal vertebral plexus that drain into the torcular herophili




Cavernous Sinus Anatomy And Surgical Approaches



Dural Venous Sinuses Cavernous Sinus Dr N Mugunthan
Midvenous phase Best phase of overall picture, where you can see veins and dural sinuses well (only lateral ventricular veins and dural sinuses are better seen in late phase) Medial (blue) and lateral (red) cortical surface vessels are well seen, as well as the dominaint superficial sylivan system (purple) draining into the inferior temporal vein (pink) The temporal pole veins (dashedCerebral venous system anatomy J Pak Med Assoc 06 Nov;56(11)5169 Authors which drain to deep veins These drain, in turn, to the venous sinuses The superficial cerebral veins can be subdivided into three groups These are interlinked with anastomotic veins of Trolard and Labbe However, the superficial cerebral veins are very variable They drain to the nearest dural sinusFor our purposes, the cannon holds that cavernous sinuses are paired, nonurethral dural venous structures located between the sella and Meckel caves, joined by the intercavernous venous plexus, and each individually connected to the superior opthalmic vein, the sphenoparietal sinus / superficial Sylvian veins, the superior and inferior petrosal sinuses, the pterygopalatine venous




Cerebral Venous Anatomy And Ppt Download




Dural Sinuses Ppt Powerpoint
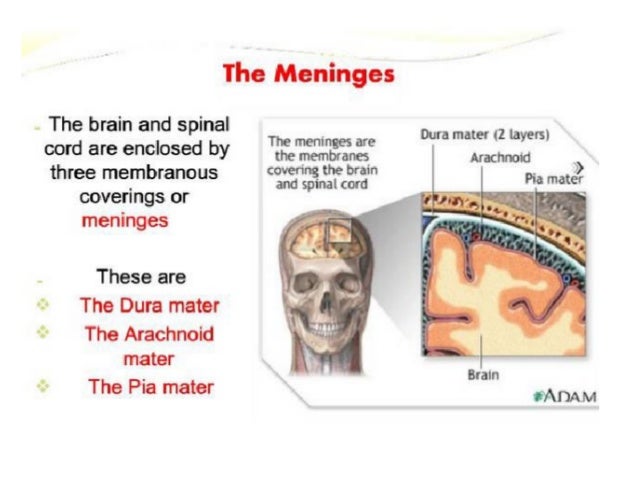
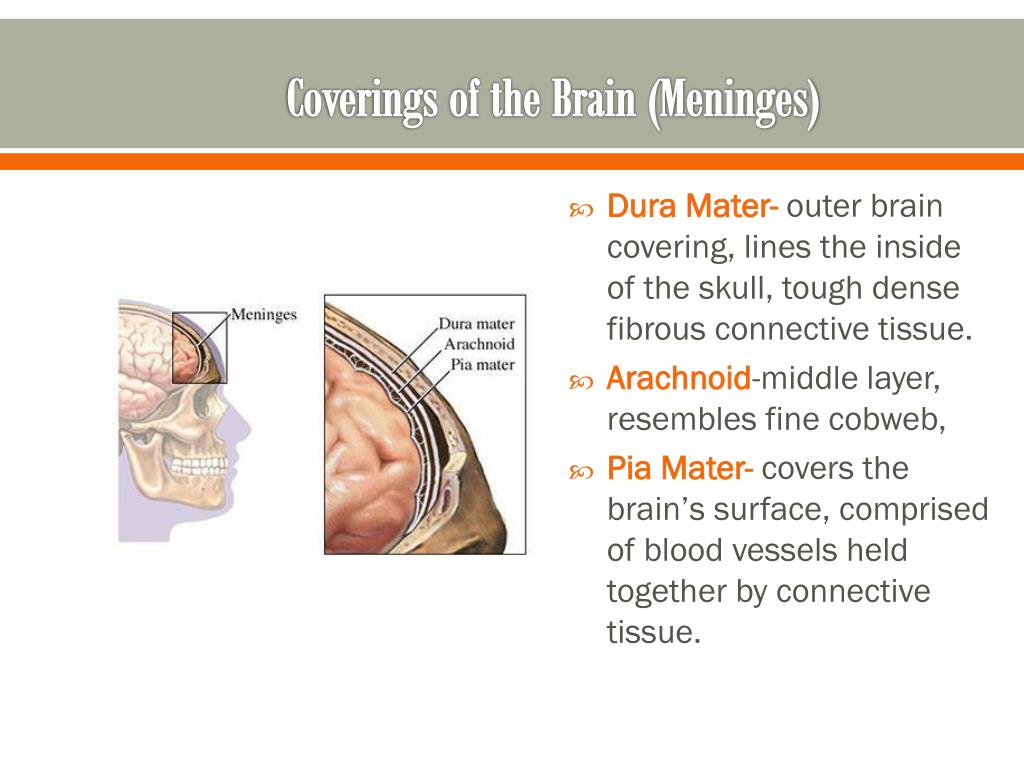
Article tools PDF 1 response Respond to this article Print Alerts & updates Article alerts Please note your email · Dural folds and cavernous sinus 1 DURAL FOLDS AND CAVERNOUS SINUS MARAVIND 2 MENINGES The interior of the cranial cavity is lined by the durameter The surface of the brain is covered by the piameter The dura is separated from the arachnoid by subdural space The arachnoid is separated from the pia by subarachnoid space (CSF) Between these two lies · Venous sinuses are common in the tentorium cerebelli In this study, they were observed in 86% of the cases They can be classified into three types, based on their location, size, configuration, and pattern of drainage The medial onethird




Venous Sinuses




Dural Folds Venous Sinuses Youtube
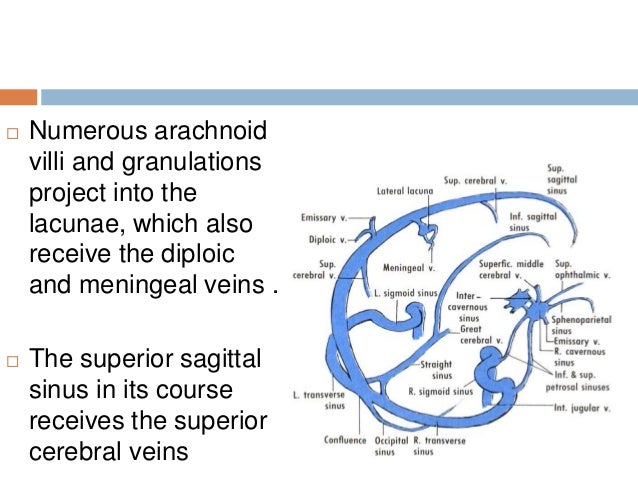
Answers A Inferior sagittal sinus B Superior sagittal sinus C Torcula heterophili (confluence of the sinuses) D Transverse sinus E Sigmoid sinus Notes Cite this as BMJ 11;343d74 View Abstract Tweet Widget; · Dural venous sinuses 3 Characteristic feature of dural venous sinuses • Lined by endothelium, no muscular coat & valveless • Collect blood from brain,meninges, orbit,internal ear & diploe • Connected to valveless emissary veins to maintain the internal & external venous pressure • Projection of arachnoid granulation into it for CSF · Changes in the appearance of venous sinuses after treatment of disordered intracranial pressure Neurology 04;



Dural Sinuses




Lufukuja G 1 Meninges And Dural Venous Sinuse 3 6 Ppt Download
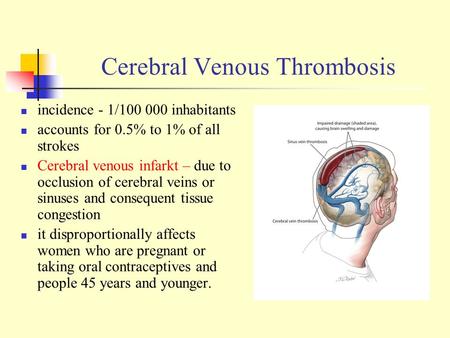
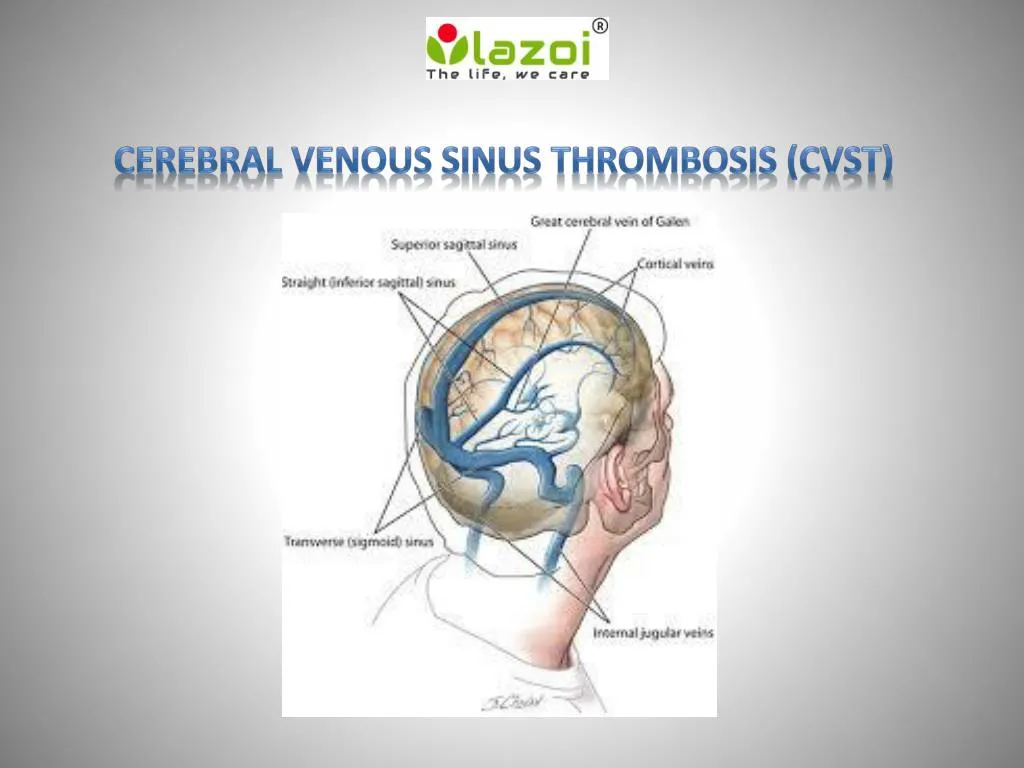
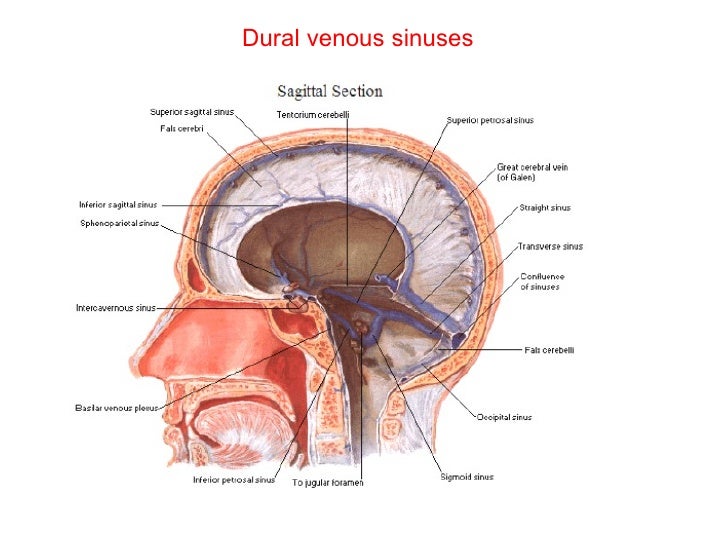
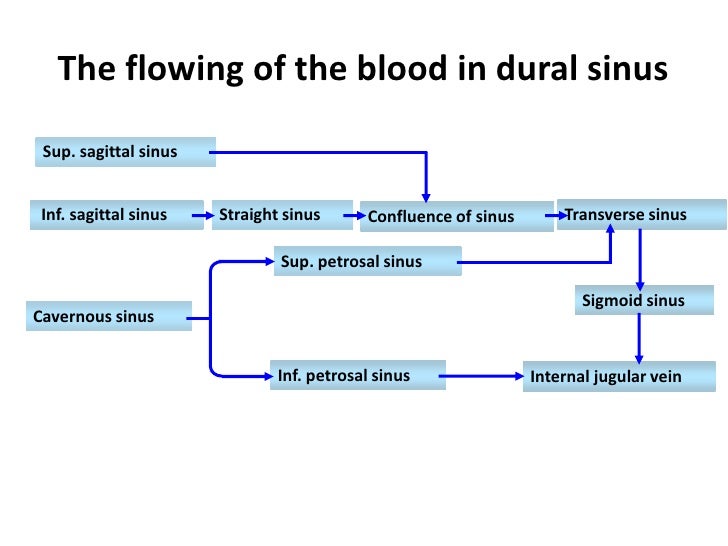
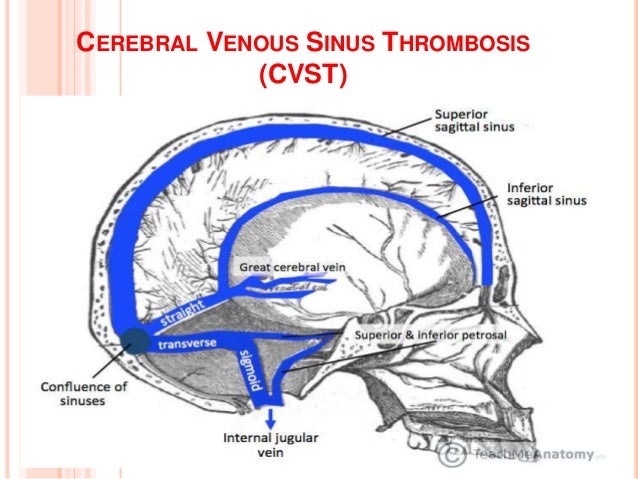
The dural venous sinuses are valveless venous channels found between the endosteal and meningeal layers of the dura mater The network of dural venous sinuses usually comprises a superior sagittal sinus, an inferior sagittal sinus, a straight sinus, a confluence of sinuses (torcular Herophili), a pair of transverse sinuses, a pair of sigmoid sinuses, a pair of cavernous sinuses,Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST) Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) is the presence of acute thrombosis (a blood clot) in the dural venous sinuses, which drain blood from the brain Symptoms may include headache, abnormal vision, any of the symptoms of stroke such as weakness of the face and limbs on one side of the body, and seizuresThis video provides a walkthrough of the dural venous sinuses (eg transverse sinus, cavernous sinus) You can follow along using our free written guide wit



Dural Venous Sinuses Cavernous Sinus Dr N Mugunthan



Dural Venous Sinuses 4 27 17 Lufukuja G Ppt Video Online Download
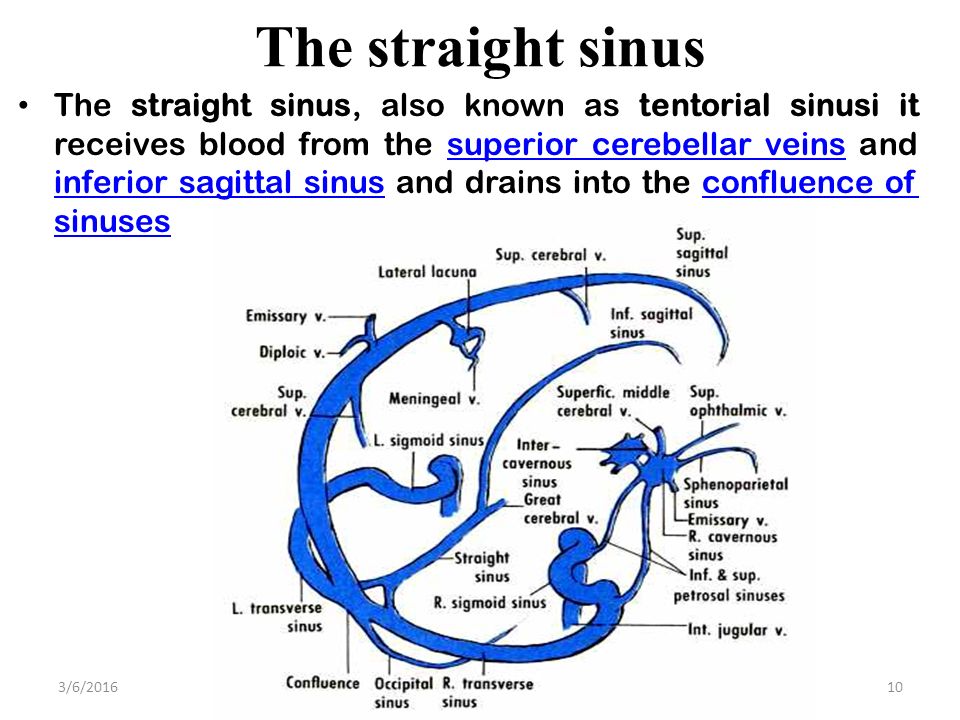
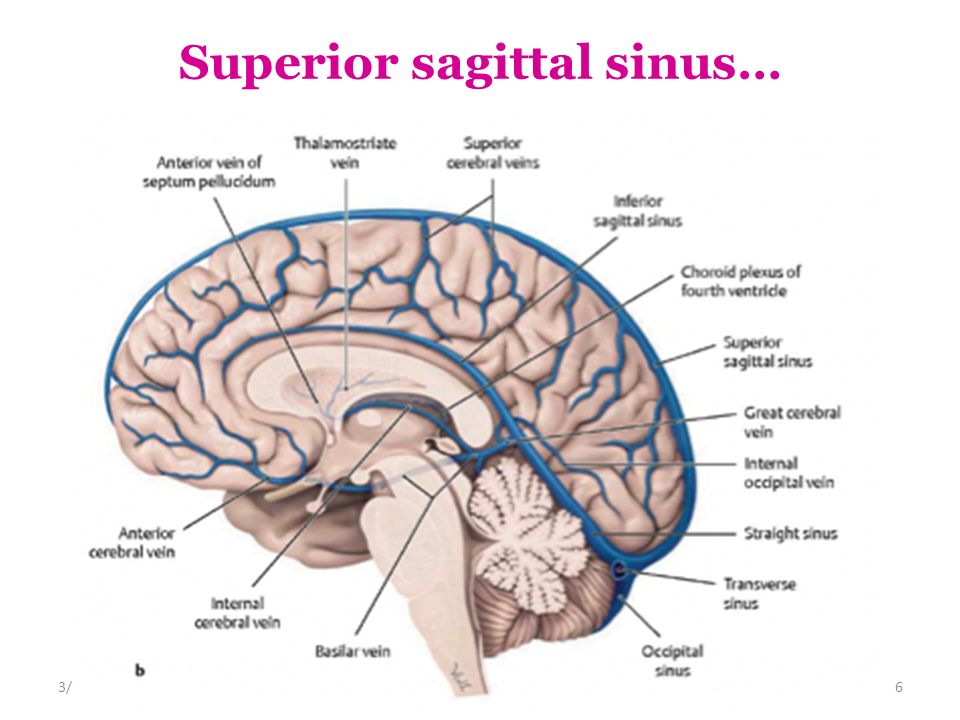
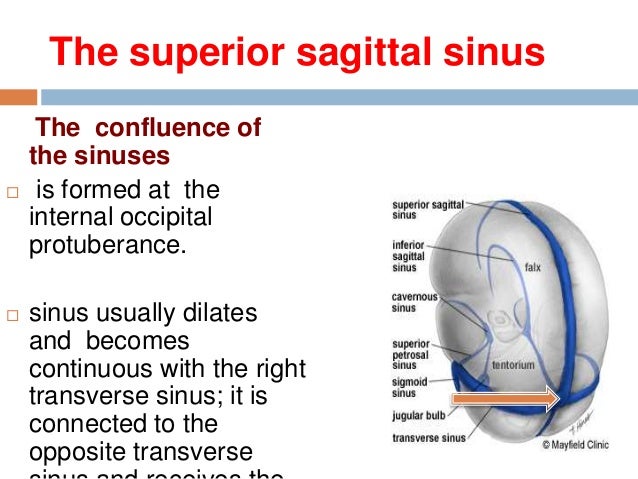
· Dural Sinus CVT Anatomy Sagittal contrast material–enhanced maximum intensity projection MR venogram shows the dural sinuses and the deep venous system It includes the superior sagittal sinus (1), inferior sagittal sinus (2), transverse sinuses (3), sigmoid sinuses (4), internal cerebral veins (5), Rosenthal veins (6), vein of Galen (7), and straight sinus (8) Figure 1Anatomy and Function of the Dural Venous Sinuses See online here The dural venous sinuses (DVS) are venous blood reservoirs located between the 2 layers of the dura mater The absence of lymphatic drainage in the brain places the venous outflow system means that the DVS is critically important This article provides an overview on dual venous sinuses and then focuses onThe dural venous sinuses develop from a widespread venous network, which allows for multiple variations Insufficient knowledge on these variations can lead to misdiagnosis and can complicate interventional neurosurgical procedures It is therefore important to understand not just the anatomy of the most consistent presentation of the dural sinuses but also the variant anatomy



Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Ppt Video Online Download




Dural Venous Sinuses 4 27 17 Lufukuja G Ppt Video Online Download
THEORY OF DURAL VENOUS SINUS VIDEO https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=Ebw3OwEQKtcTRANS CRIBRIFORM APPROACH VIDEO https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=9v_C94Bwo8s& · Dural Venous Sinuses Of The Brain Diagram In this image, you will find superior sagittal sinus, falx cerebri, inferior sagittal sinus, straight sinus, cavernous sinus, transverse sinuses, sigmoid sinus, jugular foramen, right internal jugular vein in it Our SECOND youtube film is ready to run Please subscribe our youtube channel to support us!Don't study it, Osmose it



Ppt Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Cvst Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



15 Dural Venous Sinuses
Anatomy figure at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center – "Venous dural sinuses" CavernousSinus at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) lesson2 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) Atlas image n3a8p1 at the University of Michigan Health System; · The anatomical diversity in the dural venous sinuses is significant The practicing neuroradiologist must have a thorough understanding of dural venous sinus architecture and typical anatomic variations to distinguish between normal and pathologic situations We use an imagebased method to evaluate dural venous sinus architecture as well as highlight frequentIn this tutorial we will review the anatomy and configuration of the dural venous sinuses We will be learning about the folllowing structures Superior sag



Meninges Dural Venous Sinuses Ppt Video Online Download




Dural Venous Sinuses 4 27 17 Lufukuja G Ppt Video Online Download
57 Curé JK, Van Tassel P, Smith MT Normal and variant anatomy of the dural sinuses Semin Ultrasound CT MR 1994;The dural venous sinuses (also called dural sinuses, cerebral sinuses, or cranial sinuses) are venous channels found between the endosteal and meningeal layers of dura mater in the brain They receive blood from the cerebral veins, receive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the subarachnoid space via arachnoid granulations, and mainly empty into the internal jugular vein•Extensive dural venous sinus thrombosis involving the entire superior sagittal sinus, right transverse and sigmoid sinuses •Partial thrombosis of the left transverse/sigmoid sinuses and several parasagittal cortical veins Upon arrival to Rush •Somnolent, but easily arousable •Complains of severe headache •Fully oriented •Intact cranial nerves •Fundoscopy shows blurred




Cerebral Venous Anatomy And Ppt Download
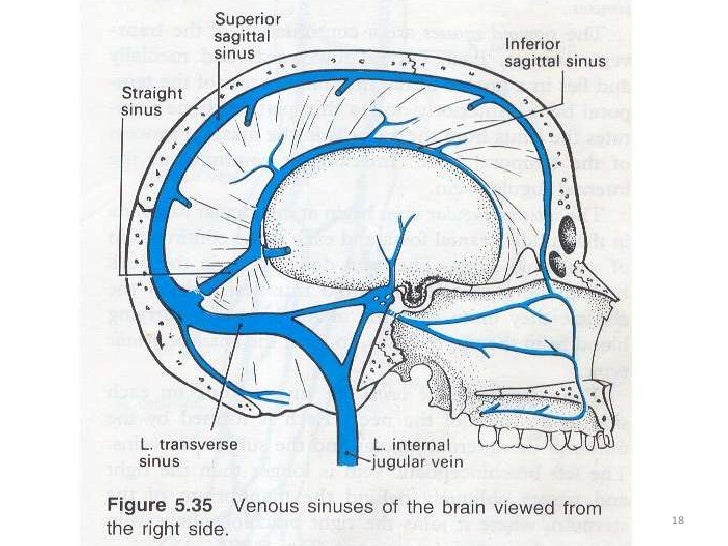



Venous Sinuses
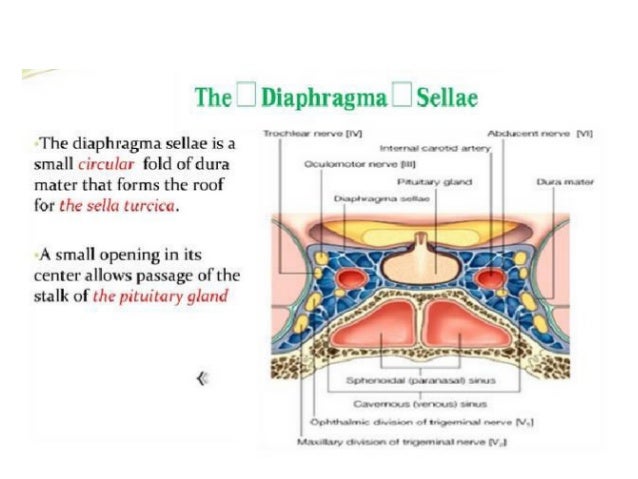
· The dural venous sinuses are located between the two layers of dura mater They are responsible for the venous drainage of the cranium and empty into the internal jugular veins The dura mater receives its own vascular supply – primarily from the middle meningeal artery and vein It is innervated by the trigeminal nerve (V1, V2 and V3)




Gmegjdddoez0zm
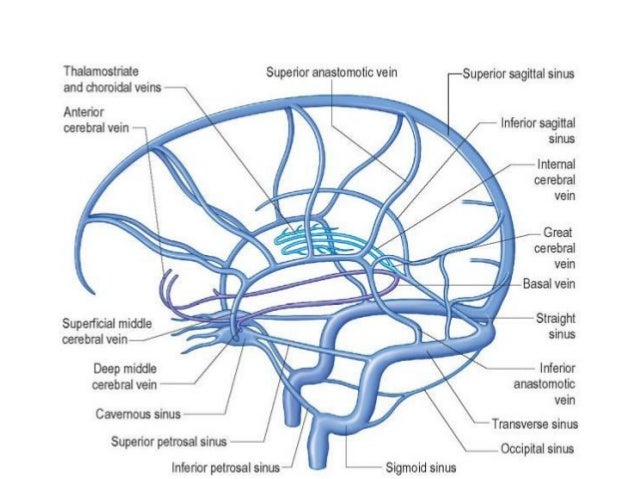



Dural Venous Sinuses
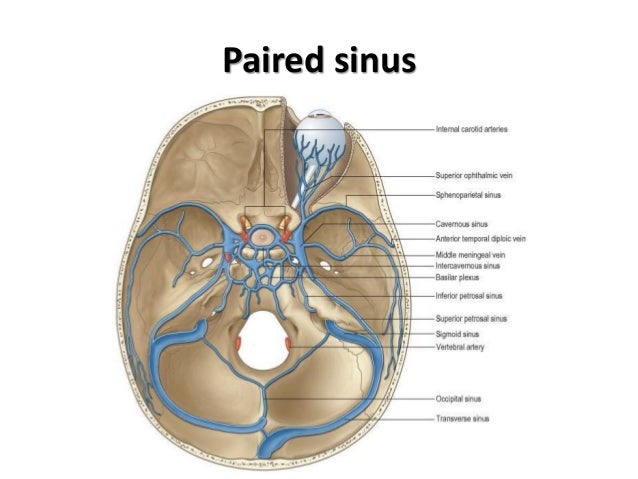



Dural Venous Sinuses



1
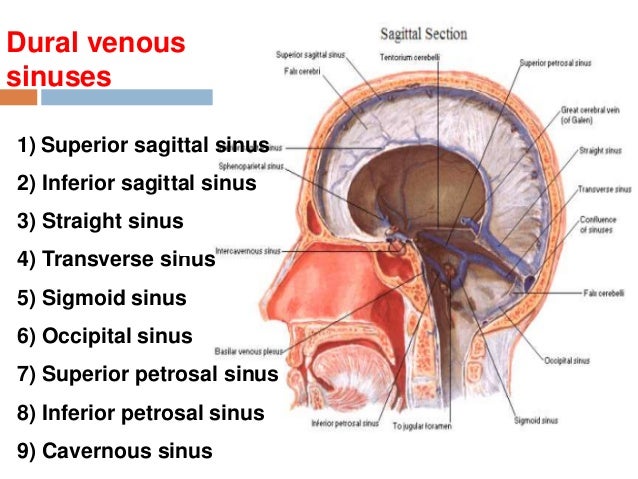



15 Dural Venous Sinuses
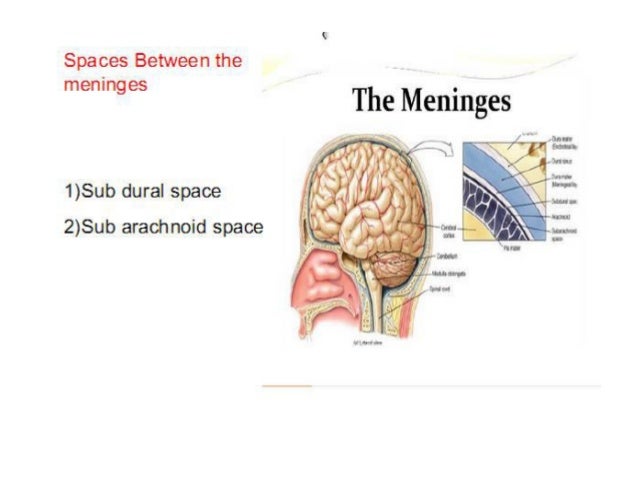



Dural Venous Sinuses




Presentation1 Ppt On Menengies Finalised




Dural Venous Sinuses 4 27 17 Lufukuja G Ppt Video Online Download




Dural Venous Sinuses Paired And Unpaired Venous Sinuses Anatomy Qa
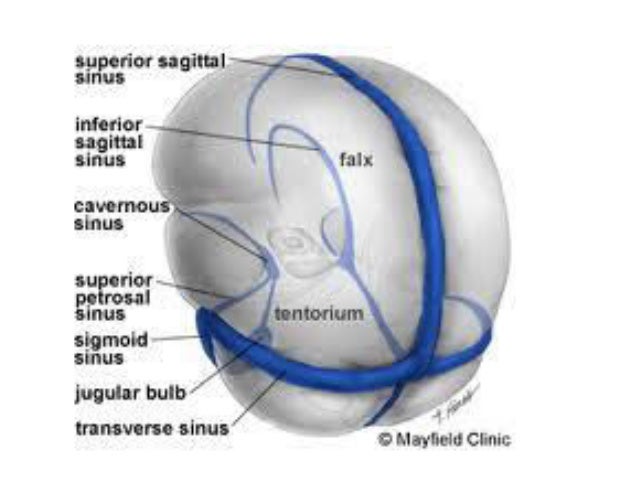



Ehcahyp Od6aym




Dural Venous Sinuses 4 27 17 Lufukuja G Ppt Video Online Download
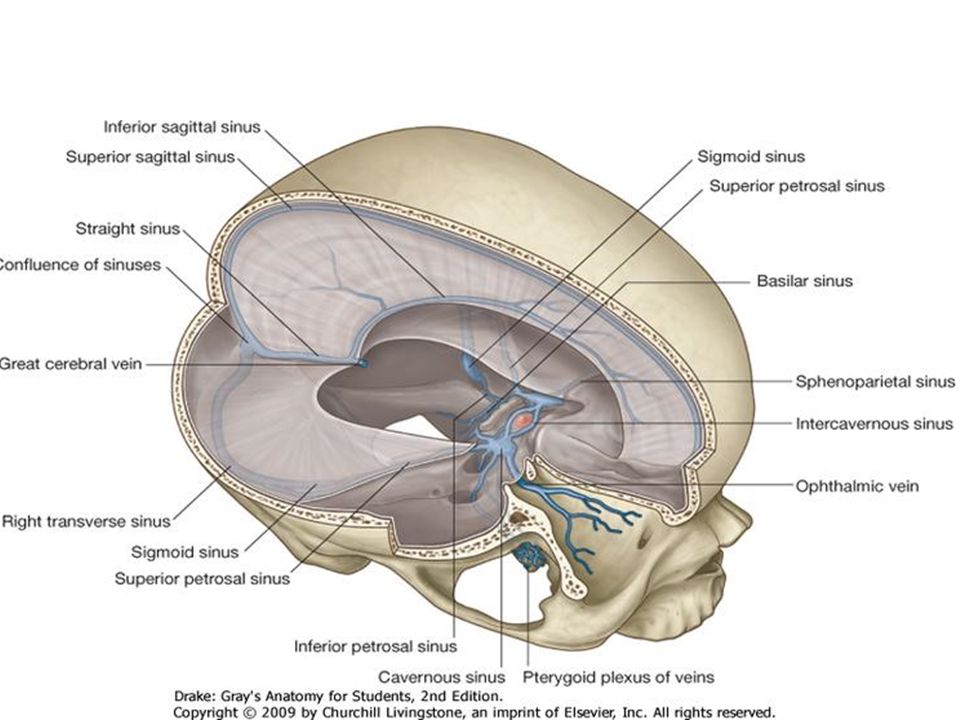



Dural Venous Sinuses 4 27 17 Lufukuja G Ppt Video Online Download




Dural Venous Sinuses 4 27 17 Lufukuja G Ppt Video Online Download




Pin On Orl



1




Cerebral Venous Anatomy And Ppt Download




Superior Sagittal Sinus And Transverse Sinus Thrombosis Ppt Video Online Download
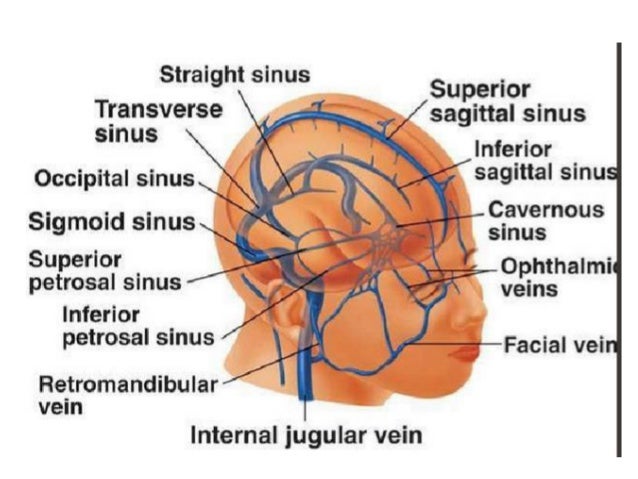



Dural Venous Sinuses



Dural Venous Sinuses Cavernous Sinus Dr N Mugunthan



1




Ppt Meninges And Cerebrospinal Fluid Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Presentation1 Ppt On Menengies Finalised




Meninges Dural Venous Sinuses Ppt Video Online Download




Cerebral Venous Anatomy And Ppt Download




Demo V Meninges And Csf Ppt Video Online Download Basement Membrane Facial Nerve Medical Anatomy




Cerebravascular Anatomy Venous System Pathologies Ppt Download




Pdf Draf Iii Frontal Sinus Surgery For The Treatment Of Pott S Puffy Tumour In Adults Our Case Series And A Review Of Frontal Sinus Anatomy Risk Factors




Cerebral Venous Anatomy And Ppt Download



Dural Venous Sinuses Cavernous Sinus Dr N Mugunthan



Venous Dural Sinuses And Cavenous Venous Sinus



Dural Venous Sinuses Cavernous Sinus Dr N Mugunthan



Dural Venous Sinuses



Dural Venous Sinuses




Dural Venous Sinuses Youtube



Dural Venous Sinuses



1




Dural Venous Sinuses Pdf Vein Primate Anatomy




Cerebral Venous Anatomy And Ppt Download




Ppt Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Powerpoint Presentation Free To Download Id 761ff1 Nzvim



15 Dural Venous Sinuses



Dural Venous Sinuses Paired And Unpaired Venous Sinuses Anatomy Qa



Venous Sinuses




Cerebral Venous Thrombosis




Cerebral Venous Thrombosis




Dural Venous Sinuses 4 27 17 Lufukuja G Ppt Video Online Download



Dural Venous Sinuses Cavernous Sinus Dr N Mugunthan



Ppt Coverings Of The Brain Meninges Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Ehcahyp Od6aym




On The Left A An Axial Ct Scan Shows A Ppt Arrow And Air Behind Download Scientific Diagram




Dural Venous Sinuses Paired And Unpaired Venous Sinuses Anatomy Qa



Venous Sinuses



Dural Sinuses



Dural Venous Sinuses




Dural Venous Sinuses




The Head Skull And Meninges Ppt 1 Flashcards Quizlet




Brain Ii And Cranial Nerves 1 Ppt Gross Anatomy Of The Brain Cranial Nerves Ii Human Anatomy Physiology 1 2 Brain Stem Mesencephalon Anterior Side Course Hero




Dural Venous Sinuses 4 27 17 Lufukuja G Ppt Video Online Download




Current Endovascular Strategies For Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Report Of The Snis Standards And Guidelines Committee Journal Of Neurointerventional Surgery




Ppt Diagnosis And Management Of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Powerpoint Presentation Id



Dural Venous Sinuses




Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis For Radiology Imaging



Venous Dural Sinuses And Cavenous Venous Sinus




Epos Trade



Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Cvst Causes Risks Complicatio




References In Cerebral Vascular Anatomy And Physiology Surgery Oxford International Edition



15 Dural Venous Sinuses




Radiological Imaging Of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Ppt Video Online Download



Dural Venous Sinuses Cavernous Sinus Dr N Mugunthan




Meninges Dural Venous Sinuses Ppt Video Online Download




Dural Venous Sinuses Cavernous Sinus Dr N Mugunthan




Pearls And Pitfalls In The Magnetic Resonance Diagnosis Of Dural Sinus Thrombosis A Comprehensive Guide For The Trainee Radiologist Journal Of Clinical Imaging Science
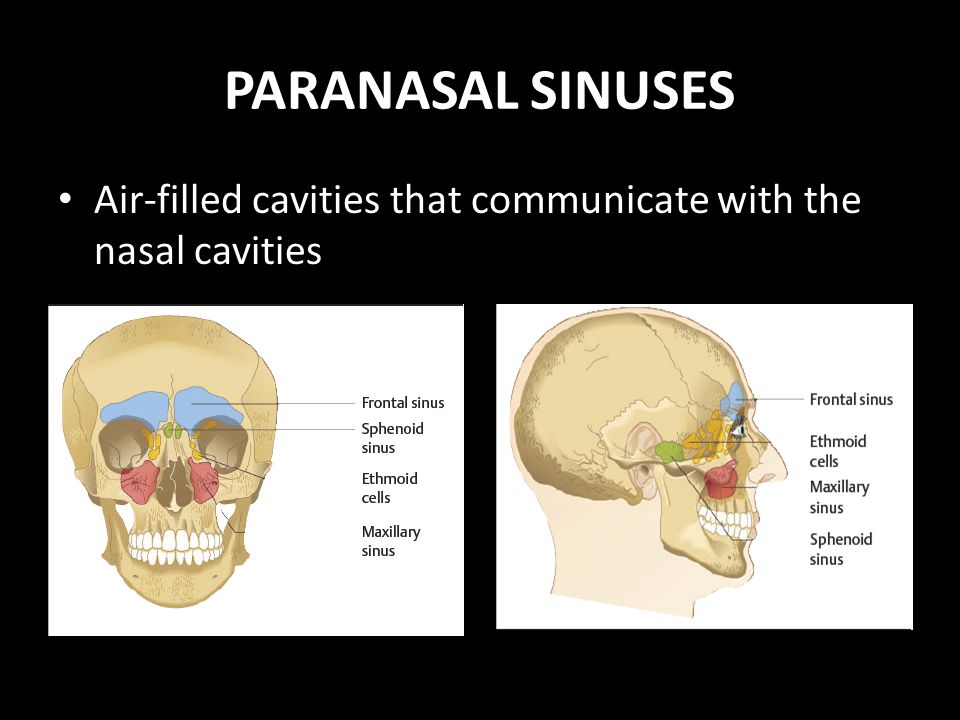



Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy Physiology And Diseases Ppt Video Online Download



Dural Venous Sinuses Cavernous Sinus Dr N Mugunthan




Ppt Sinus And Fistula Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




15 Dural Venous Sinuses



Cerebral Venous Anatomy And Ppt Download




Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Treatment
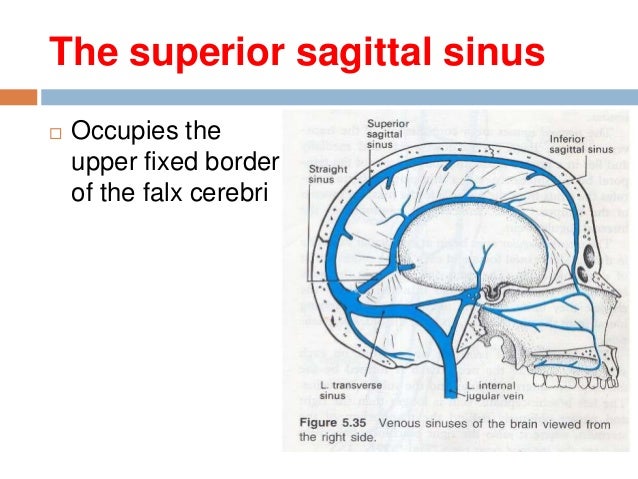



15 Dural Venous Sinuses


コメント
コメントを投稿